2011/07/14
High-Reliability RTOS to fly toward Space

The high-reliability Real Time OS (RTOS) developed by JAXA's Engineering Digital Innovation (JEDI) Center will be launched towards space at first by carried with H-IIB launch vehicle #3*. This RTOS works on HR5000, the microprocessor for space, included in new Guidance Control Computer (GCC) and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) aboard the launch vehicle.
This RTOS, conforming to Micro-ITRON4.0 and developed within the framework of TOPPERS project, is composed of the HRP(High Reliable Profile)Kernel, that was developed in co-operation with the Embedded and Real-Time Systems Laboratory, Graduate School of Information Science, Nagoya University and the Safety Kernel that was originally developed to insure safety by JEDI center. The RTOS has a function to increase whole spacecraft system reliability, such as the mechanism to prevent influences to other software even if some trouble takes place in one software.
JEDI center has been proceeding R&D of this new RTOS and the RTOS verification method in order to increase reliability of RTOS since 2003. This R&D was finished in 2007 as originally planned, but after that, we started some measures to promote practical uses, such as preparing development documents and development environment tools for users, and fulfilling inquiry correspondence system. As a result, this RTOS was chosen for new Guidance Control Computer (GCC) and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) of H-IIA/H-IIB launch vehicle.
At present, JAXA continues the final inspection for space flight during the H-IIB launch vehicle development works including system testing of equipment carrying RTOS. JEDI center is supporting the preparation aiming at successful first flight.
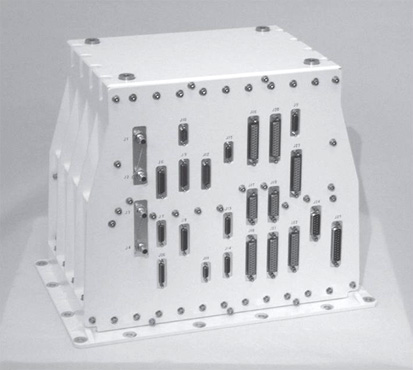
Appearance of new Guidance Control Computer (GCC)
*The H-IIB launch vehicle #3 will launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle “KOUNOTORI” (HTV) #3 in order to deliver water, food, daily commodities for the crew astronauts, experimental devices, etc. to the International Space Station (ISS) flying approximately 400 km high orbit.

